Team Introduction

Team Structure
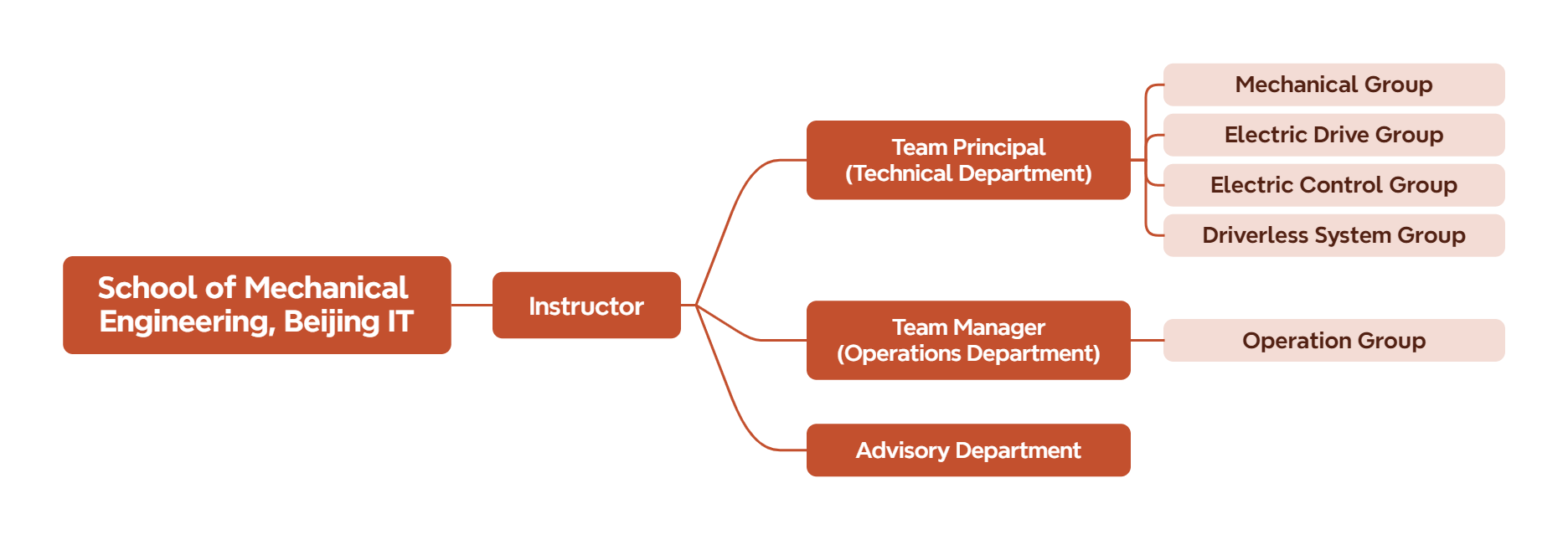
The team is affiliated with the School of Mechanical Engineering of Beijing Institute of Technology. Its members come from different schools of our university and are composed of four technical groups and one operation group.
Mechanical Group
The Mechanical Group is mainly responsible for the design of the mechanical structure of the racing car, the modification of the wire – controlled chassis, and the vehicle assembly. It has several subsystems: suspension, braking, steering, aerodynamic kit, transmission, and final assembly. The Mechanical Group is committed to achieving the close cooperation within the suspension, steering, braking and other systems and with other systems of the racing car, enabling the racing car to have excellent handling and stability. At the same time, it ensures the adaptability of the systems and the convenience of assembly and tuning.
The mechanical structure is the skeleton of the racing car. All the vehicle systems need to be built on the chassis. Guided by the cutting – edge driverless vehicle technology and based on the competition rules, the Mechanical Group uses engineering software such as CATIA and ANSYS to design and optimize the mechanical structures of subsystems such as suspension, braking, and steering. By coordinating these subsystems, the dynamic performance and stability of the racing car are improved.
Electric Drive Group
The Electric Drive Group is mainly responsible for manufacturing and debugging the drive system of the racing car, that is, high – voltage batteries, motors, and high – voltage wiring harnesses. Our work includes manufacturing the power battery box of the racing car to provide power for the motors of the racing car; designing the layout of the vehicle’s high – current circuit to transmit high – power energy safely and reliably; debugging the motors and the supporting motor controllers to make them respond quickly to the instructions of the electronic control system and drive the racing car to run.
The power battery is the power source for the racing car to move forward. Its safety, reliability, and weight are directly related to the electrical safety and power performance of the racing car. In the process of manufacturing the battery, you will need to use drawing software such as AutoCAD and CATIA to design the structure of each part of the battery box; use simulation software such as ANSYS for simulation to prove that the strength and heat dissipation of the battery meet the requirements; learn to use carbon fiber materials to manufacture a lightweight and strong battery box; carefully select each component and take insulation measures to withstand the test of high – voltage and high – current conditions.
Electric Control Group
The electrical system is the blood vessels and nerves of the racing car. Through wiring harnesses, non – programmable logic circuits, and electronic control units, it communicates closely with the driverless system, power system, and mechanical system to fully tap the potential of the racing car.
The wiring harness is the blood vessel of the racing car, carrying the power of the vehicle and transmitting the information of the entire vehicle. Cables connect each part of the racing car into an organic whole. In the theoretical design stage of wiring harness design, you will use CAD, Catia, and professional electrical software to model the 2D and 3D layouts of the racing car wiring harness. In the practical stage, you will arrange the wiring harness on the pegboard diagram and finally conduct on – vehicle debugging. In this process, you will master the use of various electrical tools and various connectors and terminals in the automotive industry, and get to know the prototype of the vehicle electrical system architecture.
Driverless System Group
The Driverless System Group is mainly responsible for the algorithm development of the driverless system, which replaces the role of the driver on the race track and serves as a bridge from an electric racing car to a driverless racing car. We write the software architecture through the ROS system (Robot Operating System) and develop it using languages such as C++ and Python. We integrate the data of various sensors and plan the route to control the racing car to move forward.
Perception is the process in which the vehicle receives environmental data in real – time through sensors distributed throughout the vehicle and builds a map, including the processing of radar point clouds, the target detection of binocular cameras, the positioning of cones, etc. This is the key to the entire system and the basis for the operation of subsequent programs. The perception module will involve knowledge related to hardware driver writing, joint calibration, and deep learning.
Operation Group
The Operation Group is mainly responsible for the management and publicity of the team. It promotes the team’s brand and culture through various platforms and collaborates with the technical departments to complete the body painting design and peripheral product development. Here, you will be able to bring your creative ideas into reality to the greatest extent.
Network platform construction mainly includes the operation of Weibo, WeChat official accounts, websites, and the liaison and material supply of other publicity media on campus. Production and planning of publicity materials include daily work highlights, track – side shooting, etc. Design of peripheral products and body painting is carried out around team work, campus activities, and exchanges with other teams.




